Water cooled condensers absorb heat from process fluid and transfer it to a separate fluid source such as a cooling tower. This type of condenser has a lower condensing temperature than air, allowing more capacity. It also improves system reliability due to lower refrigerant discharge temperature and is lower cost.

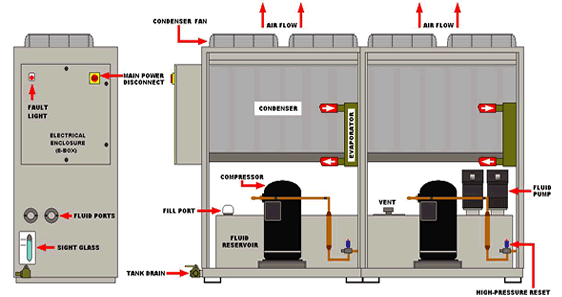
Air cooled condensers provide a refrigerant which absorbs heat from a process fluid and the condenser ultimately discharges the heat to the surrounding air. Air cooled condensers have either a horizontal or vertical discharge indicated by the location of their fans. In cooler climates, adding the economizer allows energy savings by using outside air to assist in the cooling process.